Red Sea Shipping Route: Strategic Lifeline in Global Trade and UPSC Relevance
Introduction
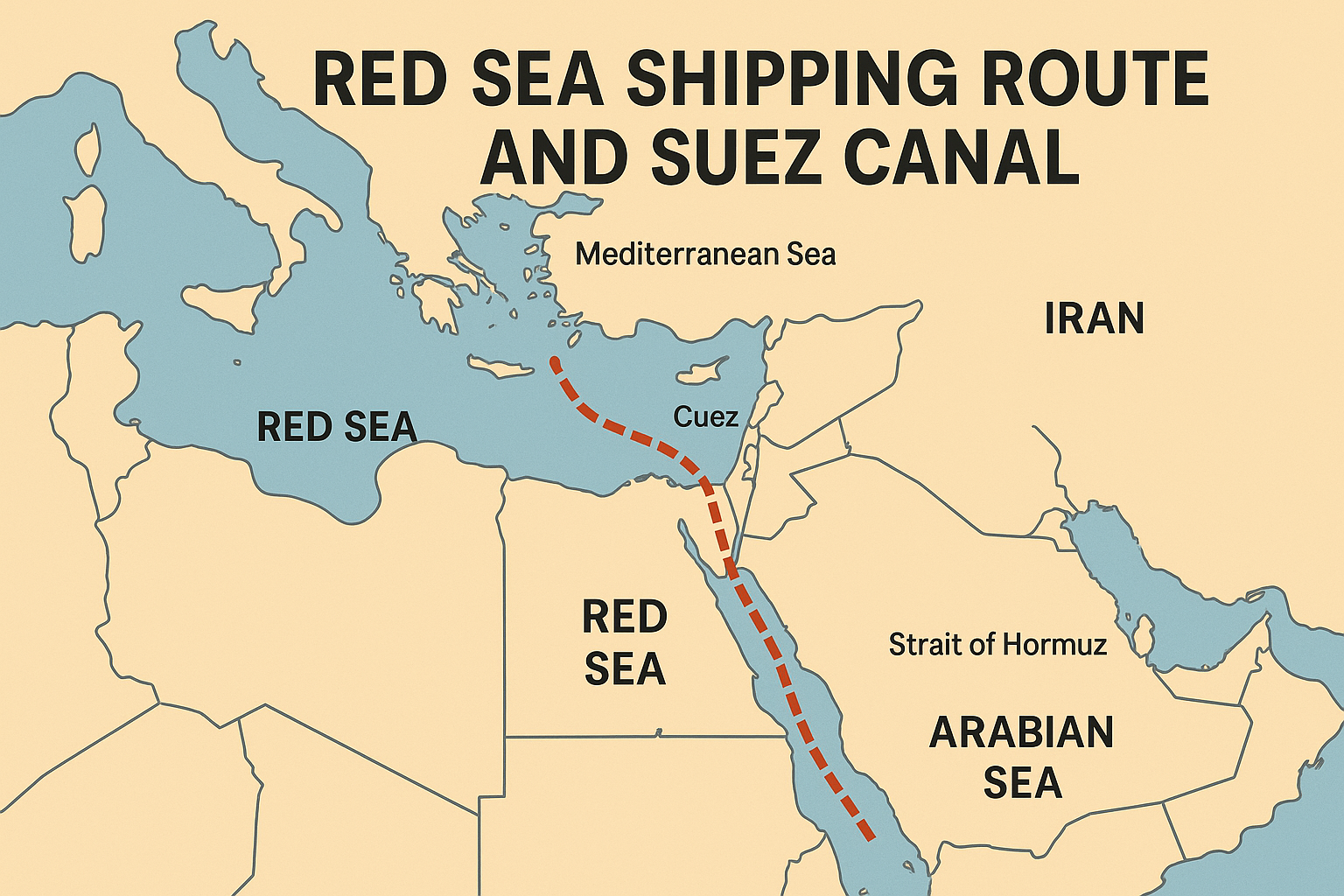
The Red Sea Shipping Route holds immense strategic, geopolitical, and economic significance, especially in the backdrop of global conflicts such as the ongoing Iran-Israel tensions. For UPSC aspirants, understanding the Red Sea Shipping Route is essential for grasping the dynamics of international trade routes, geopolitical choke points, and India’s maritime interests. In this comprehensive Knowledge Nugget, we break down everything you need to know about this vital sea route and its associated waterways including the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz.
Why in the News?
The renewed Iran-Israel conflict has once again put the spotlight on the Red Sea Shipping Route. As global shipping lines began returning to this crucial corridor from the longer Cape of Good Hope detour, tensions flared with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu declaring continued strikes on Iranian sites. The possibility of Iran retaliating by threatening the Strait of Hormuz has raised fears of disrupted trade and surging oil prices, making the Red Sea Shipping Route a key area of concern.
What Is the Red Sea Shipping Route ?
Spanning nearly 2,000 kilometers, the Red Sea Shipping Route connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean through the Suez Canal. Before the Suez Canal was built, ships had to sail around the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa, making voyages between Europe and Asia significantly longer.
The Red Sea, bordered by countries like Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen, serves as a maritime highway. It is one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world, vital for transporting oil, gas, and trade goods between the East and West.
Suez Canal: The Game-Changer
The Suez Canal, a 193-km artificial waterway opened in 1869, cuts through the Isthmus of Suez and significantly shortens the journey between Europe and Asia by up to 7,000 km. Constructed after years of financial and political hurdles by the Universal Suez Ship Canal Company under French diplomat Ferdinand de Lesseps, the canal has remained a global trade lifeline.
As of May 2025, it accounts for around 12–15% of global trade and 8–9% of the world’s energy flow. However, daily transit volumes have declined due to current geopolitical issues. PortWatch data shows a drop from over 1.3 million metric tonnes in 2024 to just 484,137 metric tonnes in May 2025.
India, in particular, is highly dependent on the Red Sea Shipping Route, with nearly 80% of its exports to Europe transiting through the Suez Canal. The rerouting of ships around Africa has escalated freight costs, denting Indian exporters’ profit margins.
Historical Context of the Suez Canal
- Ancient Foundations: Evidence suggests the region had canals dating back to the reign of Pharaoh Senausret III.
- Modern Vision: Napoleon’s efforts in 1799 were thwarted by miscalculations, but the dream was revived by Ferdinand de Lesseps.
- Operational Since 1869: After a decade of construction and numerous challenges, the canal opened to global maritime traffic.
Issues Plaguing the Suez Canal
Despite its strategic importance, the Suez Canal is also one of the world’s most congested waterways. At 193 km long, 205 meters wide, and 24 meters deep, it remains a shipping bottleneck.
The most famous incident was the Ever Given blockage in March 2021, when the giant cargo ship got stuck, halting global trade for over a week. Historically, the canal was also the epicenter of the Arab-Israeli wars of 1967 and 1973 and remained closed from 1967 to 1975.
Impact on India
India’s dependence on the Red Sea Shipping Route is substantial. Most of its Europe-bound trade passes through this corridor. The ongoing geopolitical instability has caused longer detours and increased shipping costs. With limited control over international shipping fleets, India has few short-term solutions to mitigate these impacts.
Other Strategic Maritime Routes: The Panama Canal
- Linking the Atlantic and Pacific: Completed in 1914, the Panama Canal connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans through the Isthmus of Panama.
- Engineering Marvel: It incorporates a system of locks and gravity-fed water channels due to elevation differences between oceans.
- Economic Role: Reduces travel by 8,000 nautical miles for ships between the US coasts, bypassing Cape Horn.
Like the Red Sea Shipping Route, the Panama Canal is indispensable in global trade but also susceptible to disruptions.
The Strait of Hormuz: A Parallel Chokepoint
The Strait of Hormuz lies between Iran and Oman, connecting the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea. At its narrowest, it is only 21 miles wide, with just 2-mile shipping lanes in either direction.
It is responsible for the transit of 20–25% of global oil and a significant portion of LNG, especially from Qatar and the UAE. As tensions escalate, any Iranian move to block this strait would have ripple effects across the Red Sea Shipping Route as alternative paths are sought.
UPSC Relevance: Static and Dynamic Connections
Understanding the Red Sea Shipping Route involves linking geography, economics, and international relations:
- Prelims: Location-based questions (Red Sea, Suez Canal, Panama Canal, Strait of Hormuz)
- Mains GS Paper II & III: Maritime security, global trade patterns, strategic chokepoints
- Interview: Discussing India’s trade vulnerabilities and geopolitical responses
Conclusion
The Red Sea Shipping Route is more than just a maritime path—it is a cornerstone of global trade, a geopolitical flashpoint, and a key element of India’s economic architecture. UPSC aspirants must stay updated with developments in this region and understand the strategic linkages between geography and global politics. Whether it’s the Suez Canal, the Panama Canal, or the Strait of Hormuz, these vital waterways shape the world’s economic flows and strategic decisions.
Incorporating this understanding into your UPSC preparation will not only boost your general studies but also your interview readiness.
One thought on “Red Sea Shipping Route & Suez Canal: Key Facts for UPSC Aspirants 2025”
Comments are closed.